- Exploring the interplay between phosphate signaling and jasmonate pathways in tea plants
- Researchers document Russian destruction of Ukrainian archaeological sites
- Proteins in tooth enamel offer window into ancient and modern human wellness
- Targeted interventions add five months' progress for students with SEND
- Research proposes theory to model interplay of personal and social beliefs
Who Won the U.S. Presidential Debate?

Producing future low-cost, aqueous zinc-ion batteries for sustainable, large-scale energy storage
With global demand for lithium-ion batteries fast depleting reserves of raw materials, experts are seeking safe, affordable and reliable alternatives for rechargeable batteries.
Aqueous zinc-ion batteries (AZIBs) could be the answer to producing low-cost alternatives from abundant feedstocks, and Flinders University scientists are paving the way for the production of simple and practical polymer AZIBs using organic cathodes for more sustainable energy storage technology.
"Aqueous zinc-ion batteries could have real-world applications," says Associate Professor of Chemistry Zhongfan Jia, a nanotech researcher at the College of Science and Engineering at Flinders University.
From electric vehicles to portable electronic devices, the demand and consumption of lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) have led to resource shortages and supply-chain issues of strategic metals including lithium and cobalt.
Credit: Energy Storage Materials (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.ensm.2024.103731

- September 19, 2024
ACEP accuses ECG of exchange rate manipulation leading to GH₵7bn loss

- September 16, 2024
Pictures show floods ravaging Central and Eastern Europe as death toll rises

- September 17, 2024
Where in the world is closest to becoming a '15-minute city'?


- September 17, 2024
Firefighters battle wildfires choking Brazilian capital
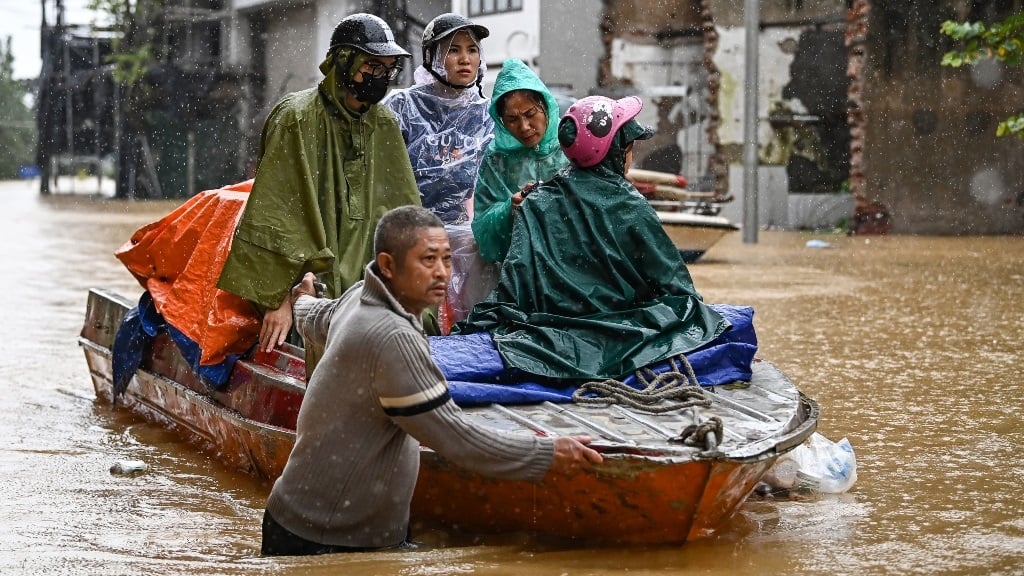

- September 14, 2024
Myanmar battles Yagi floods as Vietnam begins clear-up

- September 17, 2024
Rebuttal to article on ECG’s compliance with the Cash Waterfall Mechanism

- September 15, 2024
New plan shows Australia's hydrogen dream is still alive


- September 18, 2024
'End of an era': UK to shut last coal-fired power plant
- September 18, 2024
ECG needs a fundamental rethink

- September 18, 2024
Electric cars overtake petrol models in Norway
Subscribe to our mailing list to get the new updates!

Subscribe our newsletter to stay updated
Thank you for subscribing!


