- AI needs ‘global governance’, cannot be left to market, UN panel says
- Israeli military strikes Hezbollah as Nasrallah responds to wave of device blasts in Lebanon
- JetBlue to open airport lounges in New York and Boston in battle for big spenders
- From mortgages to auto loans, experts weigh in on when — or if — to refinance as interest rates fall
- August home sales drop more than expected, as prices set a new record
Who Won the U.S. Presidential Debate?

Harnessing the power of porosity: Advancing aqueous zinc-ion batteries and large-scale energy storage
As the global demand for energy storage solutions grows, the limitations of current lithium-ion batteries, such as safety concerns and high costs, have driven the exploration of alternative technologies. Aqueous zinc-ion batteries (AZIBs) have emerged as a promising candidate due to their inherent safety, cost-effectiveness, and environmental sustainability. However, challenges like zinc dendrite growth continue to hinder their widespread adoption. Due to these challenges, there is a pressing need to delve deeper into innovative solutions to improve AZIB performance.
The study, conducted by researchers from Tsinghua University and the University of Technology Sydney, was published in Energy Materials and Devices. It provides a comprehensive review of recent advancements in the engineering of porous zinc metal anodes for AZIBs.
The focus of the research is on the structural orderliness of these porous anodes and their critical role in enhancing battery performance. The review underscores the potential of porous zinc anodes in overcoming the limitations of traditional planar zinc anodes.
The research highlights the significant advantages of porous zinc anodes over traditional planar zinc anodes. The porous structures provide numerous nucleation sites, which reduce the nuclear energy barriers and mitigate localized charge accumulation. This, in turn, suppresses dendrite growth, ensuring a longer battery lifespan.
The study also emphasizes the role of three-dimensional porous structures in facilitating uniform electric field distribution and homogeneous ion flux, which are crucial for stable zinc deposition and stripping.


- September 18, 2024
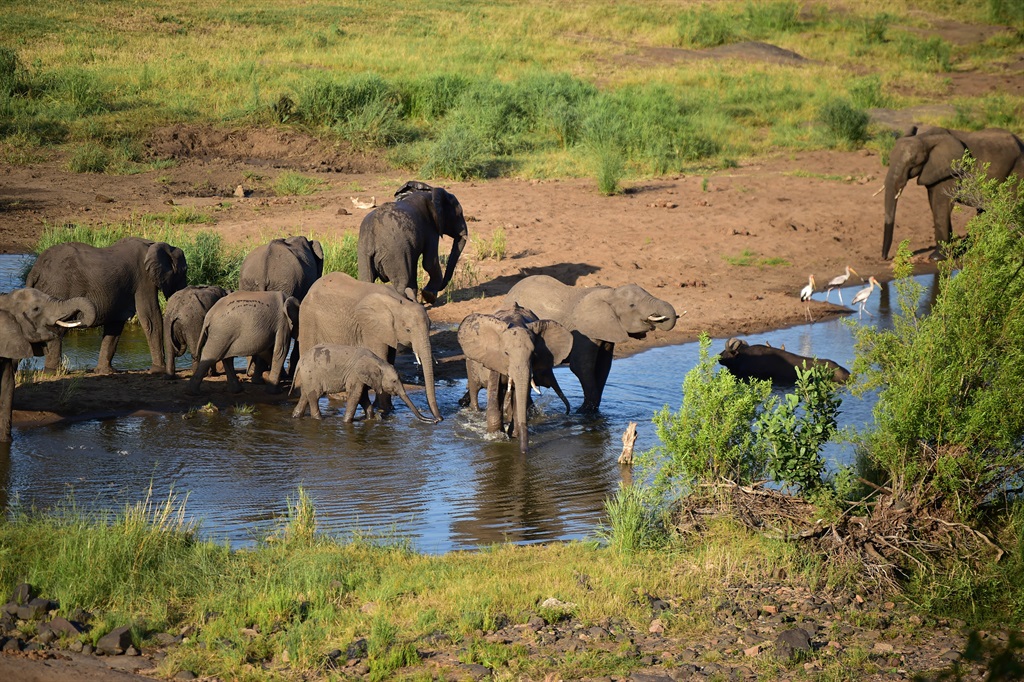
Zimbabwe to cull 200 elephants to feed people left hungry by drought
- September 18, 2024
ECG needs a fundamental rethink


- September 14, 2024
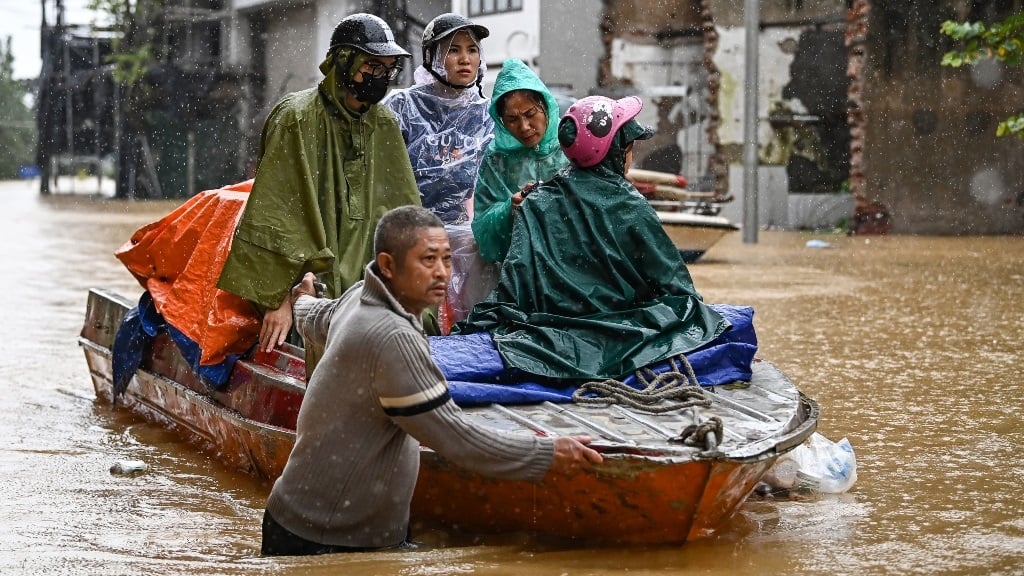
Myanmar battles Yagi floods as Vietnam begins clear-up

- September 19, 2024
PURC missed the point on Cash Waterfall Mechanism, fuel purchases – ECG

- September 16, 2024
Pictures show floods ravaging Central and Eastern Europe as death toll rises


- September 18, 2024
Electric cars overtake petrol models in Norway

- September 17, 2024
Where in the world is closest to becoming a '15-minute city'?

- September 19, 2024
ACEP accuses ECG of exchange rate manipulation leading to GH₵7bn loss


- September 19, 2024
Study outlines cost-effective paths to eliminating greenhouse gas production
Subscribe to our mailing list to get the new updates!

Subscribe our newsletter to stay updated
Thank you for subscribing!

